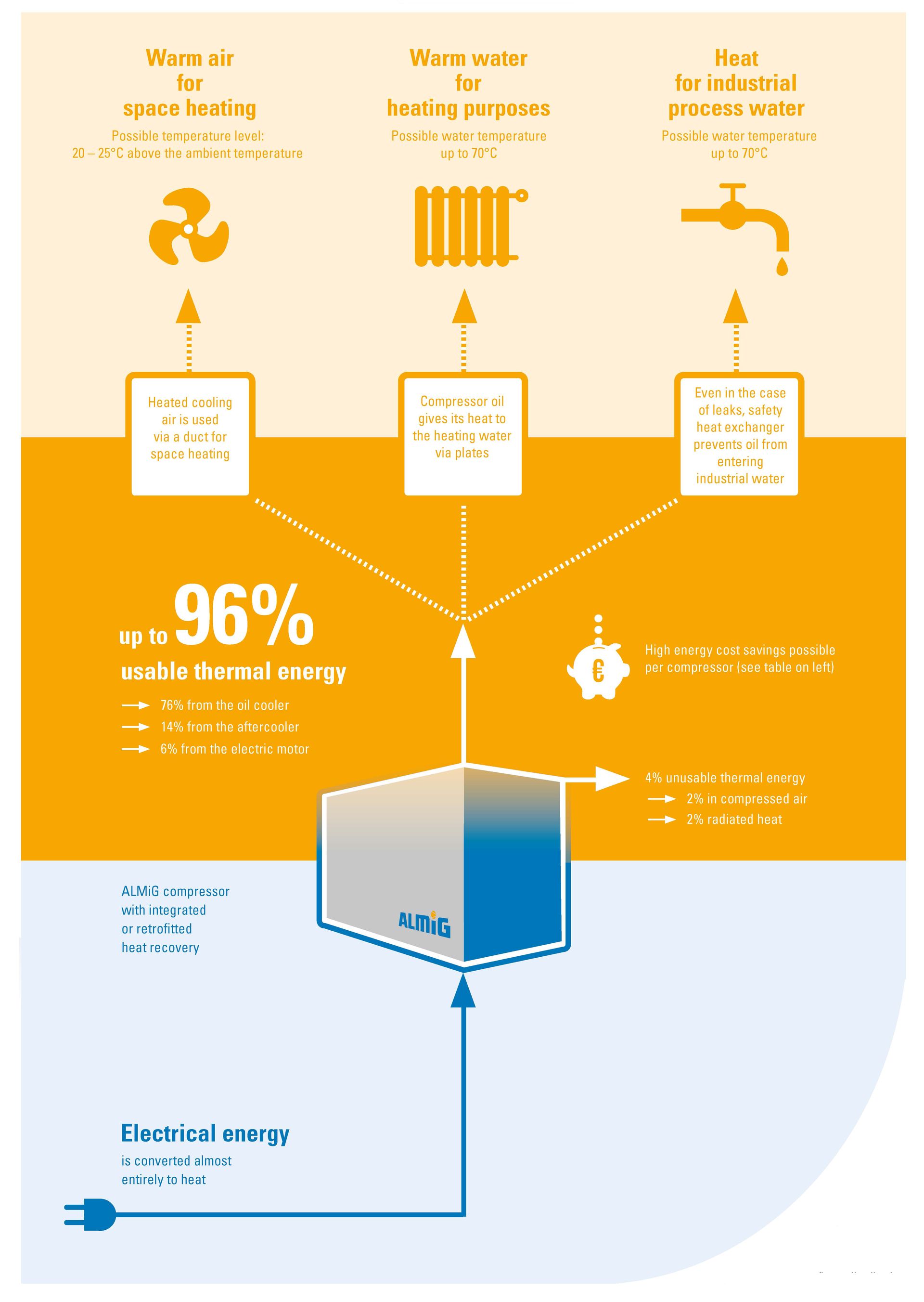
The energy consumed for compressed air generation is almost completely converted into heat.
A high energy-saving potential - after all, a compressed air station with a power requirement of 75 kW, for example, consumes approx. 300,000 kWh of electricity annually for 4,000 operating hours.
Use this energy - in the form of:
- Hot air to support space heating
- Hot water to support central heating
- Hot water for domestic use


